P.
41
Cecabank Report 2018
Corporate Culture
Solvency
One of Cecabank’s major signs of identity is its solvency. Maintaining a high
level of solvency is one of Cecabank’s strategic targets. Its speciality in
Securities Services requires these levels in order to maintain the trust of its
clients: management companies and financial institutions.
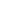
Cecabank’s CET 1 Ratio at 31 December 2018 stood at 35.83%.
Cecabank’s Board of Directors establishes the type and thresholds of
acceptable risk to achieve the corporate objectives, and it holds ultimate
responsibility for the risks incurred by the bank and performance of
its activities. This body defines the general policies with regard to the
assumption of risks. Similarly, the Board is the driving force in the corporate
risk culture, which focuses on guaranteeing efficient internal control systems
and rigorous and complete risk management and measurement processes.
Corporate risk map
The following are considered relevant in the development of the business:
•
Credit risk
is defined as the risk which affects or could affect results or
capital as a result of a breach by a borrower of the commitments set out
in any contract, or the possibility that it might not act as agreed.
•
Market risk
is defined as the risk affecting results or capital and resulting
from adverse movements in the prices of bonds, securities and exchange
rates in operations registered in the trading portfolio. In addition, it
includes foreign currency risk, defined as the current or potential risk
affecting results or capital and resulting from adverse movements in
exchange rates in the investment portfolio’s operations.
•
Interest rate risk
is the risk affecting or potentially affecting results
or capital as a result of adverse movements in interest rates in the
investment portfolio.
•
Liquidity risk
is the risk affecting or potentially affecting results or capital
as a result of the bank being incapable of meeting its payment obligations
upon maturity, without incurring unacceptable losses.
•
Operational risk
is the risk of suffering losses because of the inadequacy
or flaws of the processes, people or internal systems, or due to
external events, including legal risk. The operational scope covers the
management of the different types of operational risk affecting the bank
as a whole, including technological risk, externalisation risk and fraud
risk, among others.
CET 1 ratio
35.83%
3 | 3.2